Fungal/Mycotic Agents
Fungi can be single celled or
very complex multicellular organisms. They are found in just about
any habitat but most live on the land, mainly in soil or on plant
material rather than in sea or fresh water. A group called the
decomposers grow in the soil or on dead plant matter where they play
an important role in the cycling of carbon and other elements. Some
are parasites of plants causing diseases such as mildews, rusts,
scabs or canker. In crops fungal diseases can lead to significant
monetary loss for the farmer. A very small number of fungi cause
diseases in animals. In humans these include skin diseases such as
athletes' foot, ringworm and thrush. As far as utility as a BW
agents, fungii are unlikely to be used for their capacity for
infecting and causing serious disease in humans, however a number of
organisms in this group produce toxins (mycotoxins) which could
potentially be used. In addition there are a fair number of
fungi that could be used against crops.
The letters in (brackets)
represent the NATO military codename.
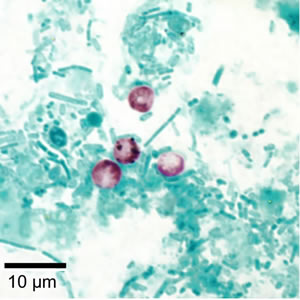
Coccidioides immitis (OC)
Coccidioides immitis - causes valley fever, also known as coccidioidomycosis. Many people who are exposed to the fungus Coccidioides are asymptomatic. Other people may have flu-like symptoms that go usually away on their own after weeks to months. If your symptoms last for more than a week, contact your healthcare provider. Symptoms of Valley fever include: fatigue, cough, fever, shortness of breath, headache, night sweats, muscle aches or joint pain, rash on upper body or legs In extremely rare cases, the fungal spores can enter the skin through a cut, wound, or splinter and cause a skin infection. Approximately 5 to 10% of people who get Valley fever will develop serious or long-term problems in their lungs. In an even smaller percent of people (about 1%), the infection spreads from the lungs to other parts of the body, such as the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord), skin, or bones and joints.