Protozoan Agents
Protozoa are microscopic organisms, usually single-celled and heterotrophic (using organic carbon as a source of energy), belonging to any of the major lineages of protists. All protozoans are eukaryotes and therefore possess a 'true,' or membrane-bound, nucleus. They also are non-filamentous (in contrast to organisms such as moulds, a group of fungi, which have filaments called hyphae) and are confined to moist or aquatic habitats. Many are symbionts of other organisms, and some species are parasitic.
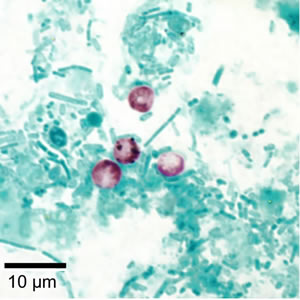
Cryptosporidium
spp. - [Cat B] cause cryptosporidiosis which is a
diarrheal and respiratory tract disease. Cryptosporidia are
protozoan, obligate intracellular parasites.There are more than
twenty members of the genus. In humans the organisms most commonly
causing disease are Cryptosporidium
hominis and C.
parvum. It is most commonly seen in children aged
between 1 and 5 years. People with weak immune systems are likely to
be more seriously affected. The most common symptom is mild to
severe watery (commonly bloody) diarrhoea but symptoms can also
include fever, abdominal cramps and vomiting. The fever is
characteristically low-grade. The incubation period is typically 2
to 10 days but may be as long as 28 days. Symptoms may last as long
as a month. Cryptosporidium infections usually aren’t serious for
someone with a healthy immune system but someone with a compromised
immune system, can have severe and long-lasting diarrhea, which can
be life-threatening. Cryptosporidiosis is contagious - it can spread
from person to person, although indirectly.
Treatment
Depending on the severity of your
symptoms and whether you have underlying conditions, your provider
may prescribe:
- Antiprotozoal medication. Nitazoxanide (Alinia®) might shorten the duration of the disease. Nitazoxanide might not work as well with patients that have a weakened immune system.
- Antidiarrheal medications. Diphenoxylate-atropine (Lomotil®) or loperamide (Imodium®) to help stop the diarrhea. This helps prevent dehydration and losing important minerals from body.
- Hydration. Special fluids to help with rehydration, and to replace electrolytes.